
;MMC.ASM 19-AUG-2001 Loren Blaney loren_blaney@idcomm.com
;Example of a driver for a SanDisk MultiMediaCard (MMC)
;Hardware design by Richard Ottosen http://www.idcomm.com/personal/ottosen
;
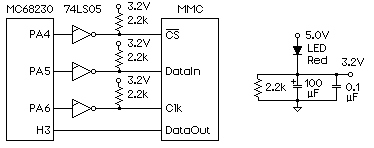
;The MMC is connected to a MC68230 parallel I/O chip. The three outputs (PA4-6)
; are inverted by 74LS05 open collector gates, which perform a level shift
; from 5.0 to 3.2 volts.
; PA4 MMC chip select (CS)
; PA5 output data to MMC (-DataIn)
; PA6 output clock to MMC (-Clk)
; H3 input data from MMC (DataOut)
;
;The following test code gives an example of how the MMC routines should be
; called. The "lcdout" procedure (not included) displays the character in the
; al register.
p1addr equ 4002h ;port A data direction register
p1adr equ 4008h ;port A data register
p1sr equ 400Dh ;status register
mmctest:
mov dx, p1addr ;set up data direction register
mov al, 70h ;1 = output
out dx, al
call InitMMC ;initialize MMC
jnc mf10 ;jump if no error detected
mov al, 'X' ;else display error message (X) on LCD
call lcdout ;(debug code)
mf10:
mov ax, 89 ;sector number to read into buffer
mov bx, offset buffer ;512-byte scratch space
call ReadSec
jnc mf20
mov al, 'Y' ;error message
call lcdout
mf20:
mov ax, 99 ;sector number to write from buffer
mov bx, offset buffer
call WriteSec
jnc mf30
mov al, 'Z' ;error message
call lcdout
mf30:
jmp $ ;hang (end of test)
;end of test code
;============================ MultiMediaCard (MMC) =============================
CSb equ 10h ;MMC CS bit
MOSI equ 20h ;MMC DataIn bit
CLOCK equ 40h ;MMC Clk bit
MISO equ 40h ;MMC DataOut bit (H3 bit 6 on p1sr)
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Initialization at power-up. Carry flag is set if an error is detected.
;
InitMMC:push ax ;save registers
push cx
push bx ;(must be last)
call RaiseCS
mov cx, 10 ;send at least 74 clock cycles
im10: call GetByte ;send 10 dummy bytes = 80 clocks
loop im10
call LowerCS
xor ax, ax ;send command 0 to put MMC in SPI mode
xor bx, bx ;SendCmd(0, 0, 95h);
mov cl, 95h ;CRC (ch=0)
call SendCmd
cmp al, 01h ;if response is not = 01h then exit
stc ; with carry flag set
jne im90
im25: call GetByte ;8 clocks to digest operation
mov al, 1 ;send command 1 (argument and CRC don't matter)
call SendCmd ;(OCR voltage profile is not used in SPI mode)
cmp al, 01h ;loop until response not = 01h
je im25
add al, 0FFh ;set carry flag if response not = 00h
im90: pushf ;save carry flag
call RaiseCS ;deselect
call GetByte ;8 more clocks to digest operation
popf ;restore carry flag
pop bx ;restore registers
pop cx
pop ax
ret
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Read sector. Carry flag is set if an error is detected.
; Inputs:
; ax = (logical) sector number [0..32767] to read from
; bx = address of 512-byte memory buffer to read sector into
;
ReadSec:push ax ;save registers
push cx
push bx ;(must be last)
add ax, ax ;bx:= sector * 2
mov bx, ax
call LowerCS
mov ax, 17 ;read command
xor cx, cx ;dummy CRC (not normally used in SPI mode)
call SendCmd
add al, 0FFh ;set carry flag if response not = 00h
jc rb90
call GetResp ;read start byte FEh
pop bx ;get buffer address
push bx
mov cx, 512 ;for 512 bytes...
rb20: call GetByte ;read byte from MMC
mov [bx], al ;store it into buffer
inc bx
loop rb20
call GetByte ;read 16-bit checksum and ignore it
call GetByte
clc ;indicate successful operation
rb90: jmp im90 ;exit
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Write sector. Carry flag is set if an error is detected.
; Inputs:
; ax = (logical) sector number [0..32767] to write to
; bx = address of 512-byte memory buffer from which to get data to write
;
WriteSec:
push ax ;save registers
push cx
push bx ;(must be last)
add ax, ax ;bx:= sector * 2
mov bx, ax
call LowerCS
mov ax, 24 ;write command
xor cx, cx ;dummy CRC (not normally used in SPI mode)
call SendCmd
add al, 0FFh ;set carry flag if response not = 00h
jc wb90
; call GetByte ;should send 8 clocks for Nwr but doesn't matter
mov al, 0FEh ;start byte
call SendByte
pop bx ;get buffer address
push bx
mov cx, 512 ;for 512 bytes...
wb20: mov al, [bx] ;get byte from buffer
inc bx
call SendByte ;send it to MMC
loop wb20
call GetByte ;send dummy 16-bit checksum (=FFFFh)
call GetByte
call GetByte ;read "data response" byte (=xxx00101b)
; only verifies CRC, which isn't used
wb30: call GetByte ;loop until not busy
cmp al, 0 ;(it can take awhile to complete a write block)
je wb30
clc ;indicate successful operation
wb90: jmp im90 ;exit
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Send command to MMC and return response byte in al
; Inputs: ax, bx, cx
;
SendCmd:or al, 40h ;send al = command
call SendByte
mov al, ah ;send ah = arg0
call SendByte
mov al, bh ;send bh = arg1
call SendByte
mov al, bl ;send bl = arg2
call SendByte
mov al, ch ;send ch = arg3
call SendByte
mov al, cl ;send cl = CRC
; or al, 01h ;LSB should be set, but it doesn't matter
call SendByte
;fall into GetResp
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Response comes 1-8 bytes after a command. Input will be 0FFh in the mean time.
;
GetResp:push cx ;save register
mov cx, 64 ;loop a maximum of 64 times (8 is not enough!)
gr10: call GetByte ;get response byte
cmp al, 0FFh
loope gr10 ;loop while byte = FFh and count not expired
pop cx
ret
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Receive a data byte from MMC
;
GetByte:mov al, 0FFh ;fall into SendByte
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Send data byte in "SPI master" fashion. Also receives a byte. Byte to send is
; in register al and received byte is returned in al. Bits are shifted MSB first
; Register ah is unchanged.
;
SendByte:
push bx ;save registers
push cx
push dx
mov bl, al ;save byte to output
mov dx, p1sr ;set up to read H3, MMC's DataOut
mov cx, 8 ;for 8 bits...
sb10: call InPort ;lower clock
and al, not CLOCK
call OutPort
and al, not MOSI ;output MSB of bl
shl bl, 1 ;shift out byte to output
jnc sb20
or al, MOSI
sb20: call OutPort
or al, CLOCK ;raise clock
call OutPort
in al, dx ;read MMC's DataOut
shl al, 1 ;copy bit 6 into high bit of bh
shl al, 1
rcl bh, 1 ;shift in received bits, MSB first
loop sb10 ;loop for 8 bits
mov al, bh ;return input byte in register al
pop dx ;restore registers
pop cx
pop bx
ret
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Raise Chip Select (CS) line
;
RaiseCS:push ax
call InPort
or al, CSb ;set CS bit
rcs80: call OutPort
pop ax
ret
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Lower Chip Select (CS) line
;
LowerCS:push ax
call InPort
and al, not CSb ;clear CS bit
jmp rcs80
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Read the MMC output port latch register
;
InPort: push dx
mov dx, p1adr
in al, dx
xor al, 70h ;compensate for inverters
pop dx
ret
;-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
;Output to MMC port
;
OutPort:push dx
mov dx, p1adr
xor al, 70h ;compensate for inverters
out dx, al
xor al, 70h ;compensate for inverters
pop dx
ret
SanDisk makes an adapter called a FlashPath that enables an MMC to be read and written in a standard 3.5-inch floppy drive. The first 32 sectors on the MMC are reserved for a partition table, which makes them inaccessible to the FlashPath. If you write to these sectors, destroying the partition table, the FlashPath will not be able to read your MMC.
DOS stores its directory starting at (logical) sector 57. (The first sector is 0.) The first file will be stored starting at sector 89.
Last updated: 17-Jan-2005